LOGICAL

Logic programming is a programming paradigm which is largely based on formal logic. Any program written in a logic programming language is a set of sentences in logical form, expressing facts and rules about some problem domain.
OBJECT ORIENTED
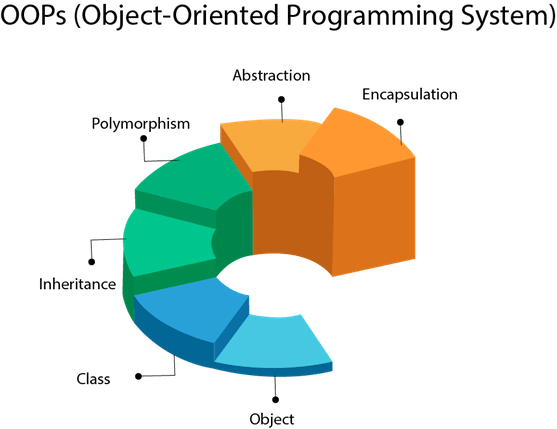
Object-oriented programming is a programming paradigm based on the concept of "objects", which can contain data, in the form of fields, and code, in the form of procedures. A feature of objects is an object's procedures that can access and
often modify the data fields of the object with which they are associated.
IMPERATIVE

In computer science, imperative programming is a programming paradigm that uses statements that change a program's state. In much the same way that the imperative mood in natural languages expresses commands, an imperative program consists of
commands for the computer to perform.
FUNCTIONAL

Functional programming (often abbreviated FP) is the process of building software by composing pure functions, avoiding shared state, mutable data, and side-effects. Functional programming is declarative rather than imperative, and application
state flows through pure functions

